Which System Controls The Coordinated Movement Of Animals? Answers.com
Class 10 Scientific discipline Notes Chapter seven Command and Coordination:Download PDF Here
Introduction
The human body is a complex machine performing tons of functions and processes to maintain and sustain life. Explore how the body controls its movements and coordinates its actions with other parts of the body and the surround by exploring notes for Class 10 Chapter 7 Control and Coordination.
The Nervous Organization
Movement in organisms
The ability of organisms to move sure body parts is movement.
When they move from one place to another, it is called locomotion.
Organisms prove movements in response to stimuli.
Introduction to control & coordination
- Organisms motion in response to various kinds of stimuli similar low-cal, heat, nutrients/food, etc.
- All the activities in animals are controlled and coordinated by the nervous and endocrine systems.
- Hormones are chemical messengers, which assist the nervous system in carrying out various functions. They are secreted past endocrine glands.
- Hormones in plants coordinate the movements.
For More Information On Nervous System, Picket The Beneath Video:

To know more well-nigh The Nervous System, visit here.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM

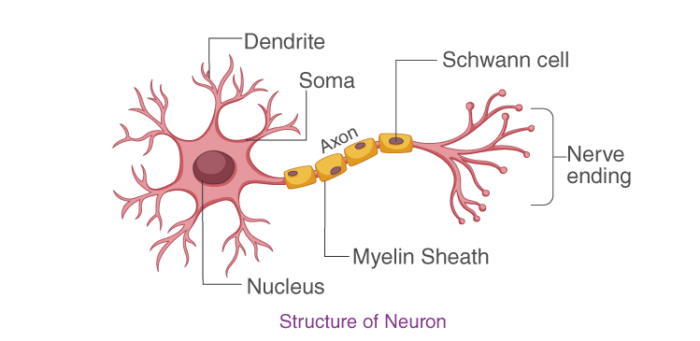
Neuron
Neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous arrangement.
- Each neuron has iii chief parts: dendrites, cyton/soma/cell body and axon.
- Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons.
- Cyton/soma processes the impulse.
- Axon transmits the impulse, either to another neuron or to muscles/glands, etc.
- Axon may be myelinated or non-myelinated.
- The impulse transmission is faster in myelinated neurons.
Central nervous system
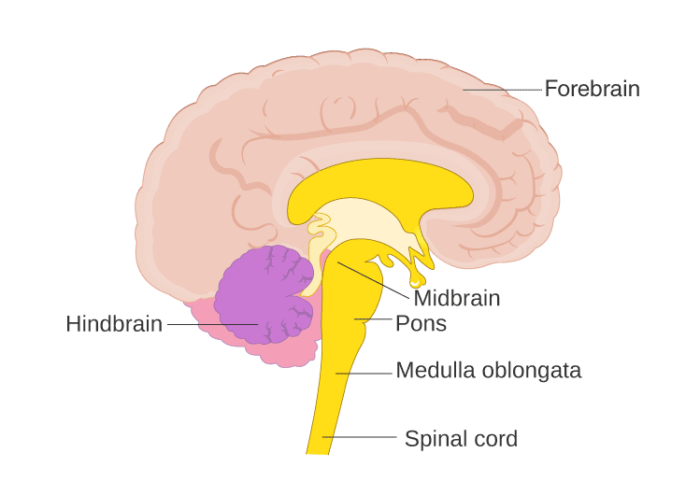
The central nervous system (CNS) is fabricated up of the brain and the spinal string. Functions of different parts of the brain are:
- The cerebrum is responsible for reasoning, logic, emotions, speech, memory, visual processing, recognition of auditory and gustation stimuli, etc.
- Cerebellum regulates and coordinates body movements, posture and balance.
- Pons relays signals from the hindbrain to the forebrain.
- Medulla Oblongata controls all involuntary movements like vomiting, sneezing, yawning, heartbeat, breathing, blood force per unit area, etc.
- Medulla oblongata continues every bit the spinal cord which runs through the vertebral cavalcade and information technology controls reflex actions.
Read more: Key Nervous System
Peripheral nervous system
- The nerves coming out from the encephalon and the spinal string constitute the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- There are 12 cranial fretfulness and 31 spinal fretfulness in humans.
Read more: Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic nervous system
- It forms a part of the PNS.
- The nerves of PNS that command the voluntary deportment of the body form the somatic nervous system.
Autonomic nervous system
- All the nerves of the PNS that control the involuntary deportment in the body grade the autonomic nervous organization. Eastward.1000. respiration, centre charge per unit, blood pressure, digestion, etc. are regulated by the autonomic nervous system.
- Ii divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous organization.
- The sympathetic nervous arrangement prepares the body for intense physical action and is often referred to every bit the fight-or-flight response, while the parasympathetic nervous system has almost the exact opposite effect and relaxes the trunk and inhibits or slows many high-energy functions.
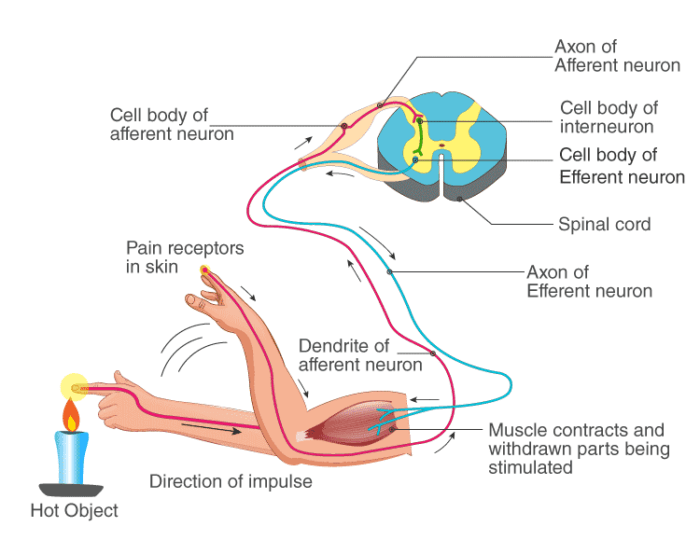
Reflex action
Reflex activity is a sudden, involuntary reaction of the body in response to stimuli.
To know more most Reflex Action, visit here.
Reflex arc
- Information technology is the path followed past an electric impulse during a reflex action.
- The impulse travels from the receptor organ to the spinal cord/brain. It is processed at that place and the information is brought back to the concerned musculus to carry out the activity.
- Thus, the receptor organ, sensory/afferent neuron, interneuron, motor/efferent neuron and effector organ are the components of a reflex arc.
Protection of CNS
The brain is protected by 3 chief layers –
- The bony skull (cranium)
- The cerebrospinal fluid
- The meninges (Dura mater, Arachnoid and Pia mater).
For More Data On Brain, Spotter The Beneath Video:

Found Hormones and Movements
Plant hormones
Control and coordination in plants are carried out past hormones.
| Plant Hormone | Part |
| Auxin | Helps in Growth of Establish Tissue |
| Cytokinin | Promotes Cell partition, delays ageing of cells |
| Gibberellins | Helps in the growth of stems, initiates seed germination, promotes flowering, cell division and seed growth subsequently germination |
| Abscisic acid | Inhibits growth and causes wilting of leaves, promotes dormancy of buds and seeds |
| Ethylene | This is a gaseous hormone which causes the ripening of fruits |
To know more about Constitute hormones, visit here.
Growth independent movements
The movements which are non growth related are called nastic movements. These movements occur in response to ecology stimuli just the direction of response is not dependent on the management of the stimulus.
- The motion in the touch-me-not plant is thigmonastic motility (movement in response to touch).

Growth-related movements in plants
The movements which are growth related are called tropic movements. These movements occur in response to environmental stimuli and the management of the response is dependent on the direction of the stimulus.
For More Information On Tropic Movements in Plants, Watch The Below Video:

To know more about Tropic Movements in Plants, visit hither.
Examples:
- Phototropic movement (light-dependent)
- Geotropic movement (gravity-dependent)
- Chemotropic movement (chemical-dependent)
- Hydrotropic movement (water-dependent)
- Thigmotropic move (bear upon dependent)
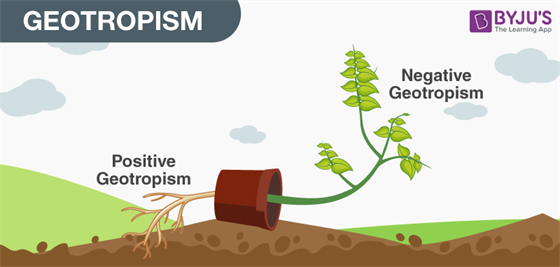
Geotropism
Movement of plant parts in response to earth'southward gravitational force is known as geotropism/gravitropism.
- Towards gravity – positive geotropism
- Away from gravity – negative geotropism
- The root grows towards gravity and shoot grows away from gravity
Phototropism
Motility of institute parts in response to light is known as phototropism.
- Towards lite-positive phototropism
- Abroad from light – negative phototropism
- Stems move towards lite and roots move abroad from calorie-free
To know more than well-nigh Phototropism, visit here.
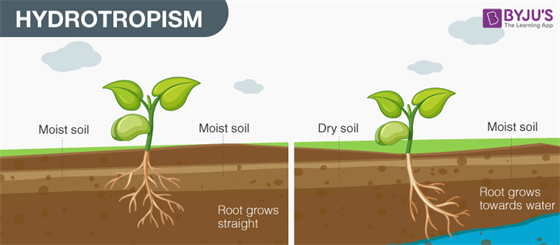
Hydrotropism
Movement of plant parts in response to water or moisture.
- Towards h2o-positive hydrotropism
- Away from water – negative hydrotropism
- Once again, root movement in search of water is positive hydrotropism
- Due east.g. move of roots towards high humidity level
Chemotropism
Movement of plant parts in response to chemical stimuli is known as chemotropism.
- Towards chemic – positive chemotropism
- Away from chemical – negative chemotropism
- The growth of pollen tube towards the ovule is positive chemotropism
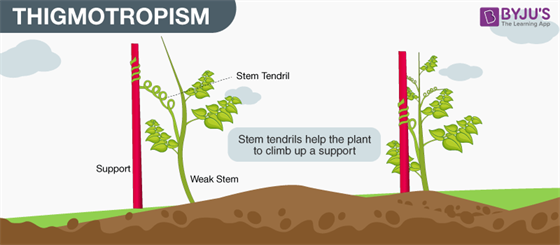
Thigmotropism
Motility of establish parts in response to touch is called as thigmotropism.
- Towards touch – Positive thigmotropism
- Away from touch – negative thigmotropism
- Movement of tendrils effectually the support is positive thigmotropism
The Endocrine System
Exocrine glands
Exocrine glands are glands that belch secretions by means of ducts, which open onto an epithelial surface.
Endocrine glands
Endocrine glands are the ductless glands which secrete hormones into the bloodstream in humans.
The endocrine glands present in the human being trunk are the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pineal, pancreas, ovary (female), testis (male), etc. Let the states now learn more virtually each of the glands below.

For More Information On Endocrine Glands, Watch The Below Video:

To know more about Exocrine glands, visit here.
Pituitary gland
- Information technology is a pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain.
- It is the main gland every bit it controls the secretions of all the other endocrine glands.
- It also secretes Growth Hormone (GH). Nether-secretion of GH causes Dwarfism and over-secretion causes Gigantism in children and 'Acromegaly' in adults.
To know more nigh Pituitary gland, visit here.
Thyroid gland
- It is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the pharynx.
- It secretes the hormone 'Thyroxine' which regulates the metabolism of the body.
- Iodine is required to synthesize thyroxine in the body.
- In the example of iodine deficiency, nether-secretion of thyroxine leads to goitre.
To know more about Thyroid gland, visit here.
Pancreas
- It is a leaf-similar gland present backside the stomach in the belly.
- It is an endocrine likewise an exocrine gland.
- Equally an endocrine gland, it manufactures 2 hormones – Insulin and glucagon. Both these hormones act antagonistically and regulate the sugar level in the blood.
- As an exocrine gland, it secretes enzymes to pause down the proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids in nutrient.
- An insufficient amount of insulin from the pancreas leads to diabetes.
To know more than about Pancreas, visit here.
Adrenal gland
- Occurs in pairs in a higher place each kidney.
- It decreases in size with age.
- Secrets the hormone adrenaline which helps in flying and fight response.
- Also secretes nor adrenaline
To know more about the Adrenal gland, visit here.
Gonads
- Gonads are the gamete-producing organs – testes in males and ovaries in females.
- The testes produce the male hormone testosterone and the ovaries produce the female hormones oestrogen and progesterone.
- Testosterone and oestrogen aid in producing gametes and are responsible for the sexual characteristics of males and females respectively.
- Progesterone is the pregnancy hormone.
To know more than about Gonads, visit hither.
Other endocrine organs
- The other endocrine organs include the hypothalamus, parathyroid, pineal and thymus glands.
To know more than about The Endocrine System, visit here.
Also Check:
- CBSE Course 10 Science Notes Chapter 6 Life Processes
- CBSE Class x Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce Notes
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- NCERT Exemplar Class ten Science Solutions for Chapter seven – Control And Coordination
- Real Numbers Class 10 Notes: Chapter 1
- CBSE Class 10 History Notes Chapter 1 – The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
Oft Asked Questions on CBSE Course ten Scientific discipline Notes Affiliate 7: Command and Coordination
What is the function of the Central nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) controls well-nigh functions of the body and mind. It consists of 2 parts: the brain and the spinal string. The encephalon is the centre of our thoughts, the interpreter of our external environment, and the origin of control over body movement.
What are some facts nigh the human brain?
ane. 60% of the human brain is composed of fat
ii. The brain contains about 100 billion neurons and 100 trillion connections
3. The texture of the encephalon is similar to that of house jelly
How many parts does the human center have?
The human being center totally consists of vii parts that work together.
Source: https://byjus.com/cbse-notes/cbse-class-10-science-notes-chapter-7-control-and-coordination/
Posted by: mahaffeymersed.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which System Controls The Coordinated Movement Of Animals? Answers.com"
Post a Comment